The thyroid gland is one of those unsung heroes in our body, small but mighty, influencing everything from our energy levels to our metabolism. If you’ve ever wondered, “What does the thyroid do?” or searched for “thyroid symptoms,” you’re not alone.
Millions of people deal with thyroid issues every year, and understanding this butterfly-shaped gland can make a world of difference in managing your health. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll dive into the thyroid’s anatomy, its crucial functions, common disorders like hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism, symptoms to watch for, diagnosis methods, treatment options, and practical tips for maintaining thyroid health. Whether you’re experiencing fatigue, weight changes, or just curious about thyroid function, this article will provide clear, actionable insights.
As a note, while we’ll touch on helpful products available on Amazon to support thyroid health, always consult a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement or regimen. Thyroid conditions can be serious, and personalized medical advice is key.
What Is the Thyroid Gland?
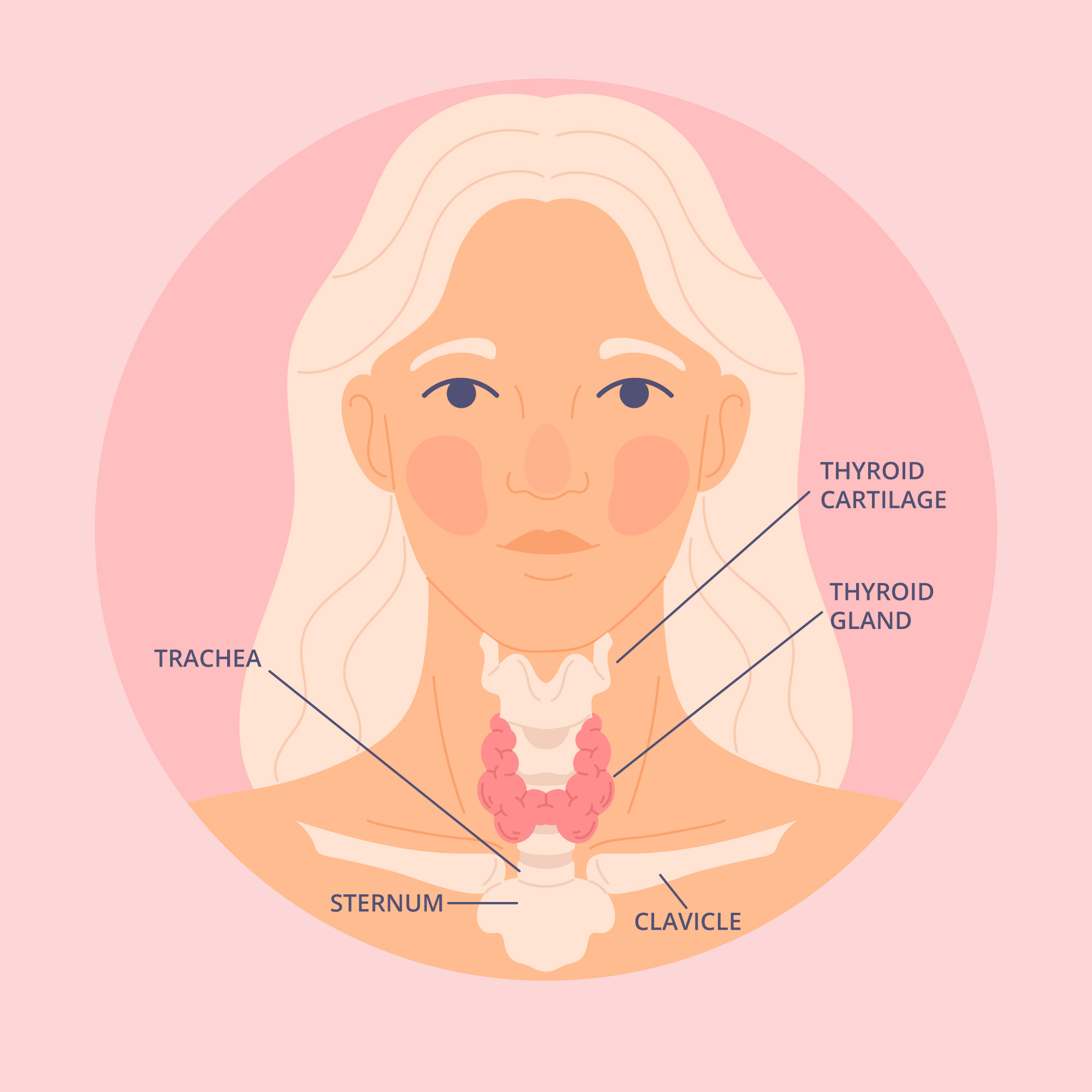
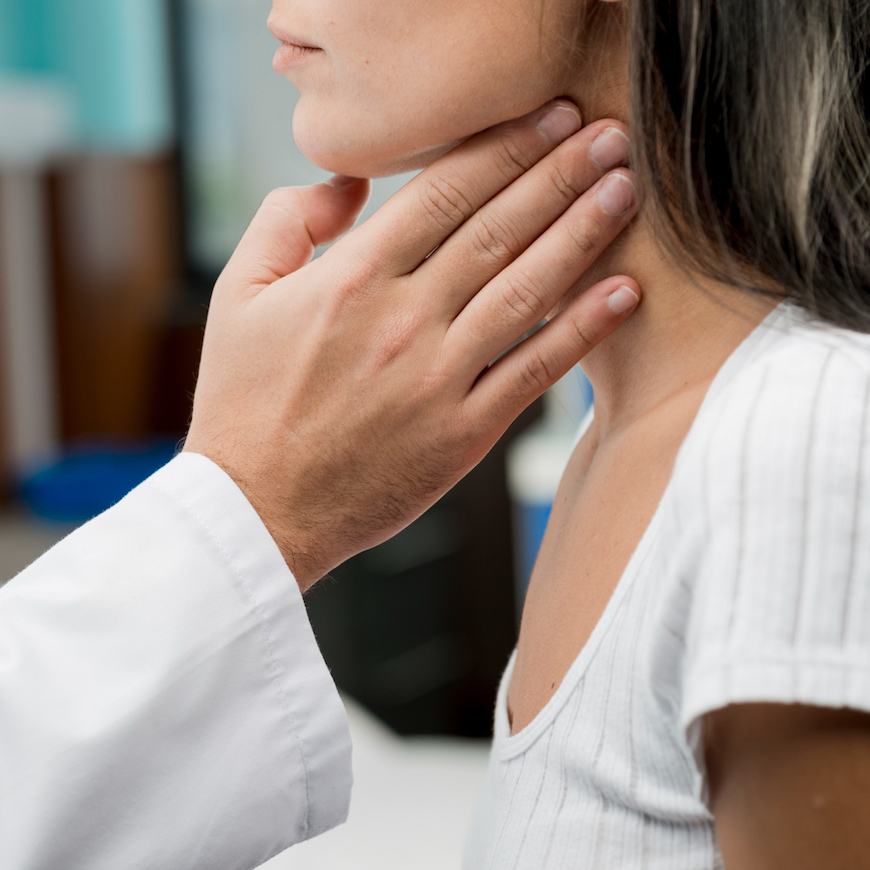
The thyroid gland is a small, endocrine organ located in the front of your neck, just below the Adam’s apple. Shaped like a butterfly with two lobes connected by a thin bridge called the isthmus, it weighs about 20-30 grams in adults. Despite its modest size, the thyroid plays a pivotal role in regulating your body’s metabolism, growth, and development.
Produced by specialized cells called follicular cells, the thyroid hormones, primarily thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), are released into the bloodstream and travel to every cell in your body. These hormones are made using iodine, which we get from our diet, and they’re essential for converting food into energy. Without a properly functioning thyroid, you might feel like your body’s engine is running on low fuel.
Learn more about Thyroid Hormones: T3, T4, and TSH
Interestingly, the thyroid is controlled by the pituitary gland in the brain, which releases thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) to signal when more or less thyroid hormone is needed. This feedback loop keeps everything in balance, but disruptions can lead to various thyroid disorders. According to health experts, about 20 million Americans have some form of thyroid disease, with women being five to eight times more likely than men to develop issues. If you’re searching for “thyroid gland location” or “thyroid basics,” this is your starting point – a gland that’s central to your well-being but often overlooked until something goes wrong.
Anatomy and Location of the Thyroid
Let’s get a bit more detailed on the thyroid’s anatomy. The gland sits wrapped around the trachea (windpipe) and is positioned just above the collarbone. It’s richly supplied with blood vessels, which is why surgeons take extra care during procedures in this area to avoid complications.
The thyroid consists of two main types of cells: follicular cells, which produce T3 and T4, and parafollicular cells (or C cells), which secrete calcitonin. Calcitonin helps regulate calcium levels in the blood, playing a role in bone health. Surrounding the thyroid are the parathyroid glands – four tiny glands that manage calcium independently but are often mentioned in thyroid discussions due to their proximity.
If you’ve ever felt a lump in your neck or experienced swelling, it could be related to the thyroid. Conditions like goiter, an enlargement of the gland, can make it visible or palpable. For those googling “thyroid anatomy diagram” or “where is the thyroid located,” imagine it as a natural necklace at the base of your throat – elegant, functional, and vital.
For a detailed anatomy breakdown, see Cleveland Clinic’s guide.
The Vital Functions of the Thyroid
So, what does the thyroid do exactly? Its primary job is to produce hormones that control your basal metabolic rate – the speed at which your body uses energy at rest. This affects weight management, heart rate, body temperature, and even cholesterol levels. Thyroid hormones are crucial during pregnancy for fetal brain development and in children for proper growth.
Beyond metabolism, the thyroid influences:
- Heart Health: It helps regulate heartbeat and blood pressure.
- Digestive System: Affects how quickly food moves through your gut.
- Nervous System: Impacts mood, concentration, and reflexes.
- Reproductive Health: Plays a role in fertility and menstrual cycles.
- Bone and Muscle Function: Ensures calcium balance and muscle strength.
Without enough thyroid hormone (hypothyroidism), your body slows down, leading to fatigue and weight gain. Too much (hyperthyroidism) revs things up, causing anxiety and rapid weight loss. For anyone researching “thyroid function explained” or “how thyroid affects metabolism,” think of it as your body’s thermostat – keeping everything running smoothly.
Thyroid health is also linked to overall wellness. Iodine deficiency, common in some regions, can impair function, which is why iodized salt is a global health staple. Selenium and zinc are other nutrients that support thyroid hormone production, highlighting the gland’s reliance on a balanced diet.
Common Thyroid Disorders and Conditions
Thyroid disorders are among the most prevalent endocrine issues worldwide. Let’s break down the main ones, including symptoms and causes, to help you recognize potential problems early.
Hypothyroidism: When the Thyroid Slows Down
Hypothyroidism occurs when the thyroid doesn’t produce enough hormones, affecting about 4.6% of the U.S. population over age 12. The most common cause is Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, an autoimmune disease where the body attacks the thyroid. Other triggers include iodine deficiency, certain medications, or radiation therapy.
Symptoms of hypothyroidism often develop slowly and can mimic other conditions, making diagnosis tricky. Common signs include:
- Persistent fatigue and weakness
- Unexplained weight gain
- Sensitivity to cold
- Dry skin and hair loss
- Constipation
- Depression or brain fog
- Muscle aches and joint pain
- Irregular menstrual cycles in women
If left untreated, hypothyroidism can lead to more severe issues like heart disease or myxedema coma. For those searching “hypothyroidism symptoms in women” or “causes of low thyroid,” early detection is crucial – especially since it’s more common in women over 60.
Hyperthyroidism: The Overactive Thyroid
On the flip side, hyperthyroidism happens when the thyroid produces too much hormone, speeding up bodily functions. Graves’ disease, another autoimmune condition, is the leading cause, often accompanied by bulging eyes (exophthalmos). Nodules or inflammation can also trigger it.
Key symptoms include:
- Rapid heartbeat or palpitations
- Unintentional weight loss despite increased appetite
- Anxiety, irritability, or tremors
- Heat intolerance and excessive sweating
- Frequent bowel movements
- Thinning hair and brittle nails
- Menstrual irregularities
Hyperthyroidism affects about 1% of Americans and can lead to complications like osteoporosis or heart arrhythmias if not managed. Queries like “hyperthyroidism treatment options” or “signs of overactive thyroid” often lead people to seek medical help promptly.
Learn more about hypothyroidism symptoms from Mayo Clinic.
Other Thyroid Conditions
- Thyroid Nodules: Lumps in the thyroid, usually benign but sometimes cancerous. About 50% of people over 60 have them.
- Goiter: Enlargement of the thyroid, often due to iodine deficiency or Hashimoto’s.
- Thyroid Cancer: Rare but treatable, with papillary thyroid cancer being the most common type. Survival rates are high with early intervention.
- Thyroiditis: Inflammation, which can be subacute (painful) or postpartum (after pregnancy).
Autoimmune factors play a big role in many thyroid diseases, and genetics can increase risk. If you’re exploring “thyroid disorders list” or “common thyroid problems,” remember that lifestyle and environment also influence outcomes.
Recognizing Symptoms and When to See a Doctor
Thyroid symptoms can be subtle and overlap with other health issues, like stress or aging. For hypothyroidism, watch for sluggishness and cold intolerance; for hyperthyroidism, nervousness and heat sensitivity. Neck swelling, voice changes, or difficulty swallowing warrant immediate attention, as they could indicate nodules or cancer.
Women, especially during menopause or postpartum, should be vigilant, as hormonal shifts can exacerbate thyroid issues. If you notice persistent changes, don’t hesitate to consult a doctor. Early screening via blood tests can prevent complications. Searches for “thyroid symptoms checklist” or “when to test thyroid” emphasize the importance of proactive health monitoring.
Diagnosis and Testing for Thyroid Issues
Diagnosing thyroid problems typically starts with a physical exam and blood tests measuring TSH, T4, and T3 levels. High TSH with low T4 suggests hypothyroidism; low TSH with high T4 indicates hyperthyroidism. Antibody tests can confirm autoimmune causes like Hashimoto’s or Graves’.
Imaging like ultrasound helps evaluate nodules, while a fine-needle aspiration biopsy checks for cancer. Radioactive iodine uptake tests assess how the thyroid absorbs iodine. For those querying “thyroid blood test results explained” or “how to diagnose hypothyroidism,” these tools provide a clear picture, guiding effective treatment.
Treatment Options for Thyroid Disorders
Treatment varies by condition but aims to restore hormone balance.
For hypothyroidism, synthetic levothyroxine (like Synthroid) is the gold standard, taken daily to replace missing hormones. Regular monitoring ensures the dose is right.
Hyperthyroidism treatments include antithyroid drugs (e.g., methimazole) to reduce hormone production, beta-blockers for symptom relief, radioactive iodine to shrink the gland, or surgery for severe cases.
Thyroid cancer often involves surgery, followed by radioactive iodine or hormone therapy. Lifestyle adjustments, like a nutrient-rich diet, support all treatments.
Always work with an endocrinologist for personalized care. Popular searches like “natural remedies for hypothyroidism” or “hyperthyroidism medication side effects” highlight the need for evidence-based approaches alongside conventional medicine.
Prevention and Tips for Thyroid Health
While not all thyroid issues are preventable, you can support your gland through lifestyle choices:
- Diet: Ensure adequate iodine (from seafood, dairy, or iodized salt), selenium (Brazil nuts), and zinc (meats, seeds). Avoid excessive soy or cruciferous veggies if you have thyroid problems, as they can interfere with hormone production.
- Exercise: Regular activity helps regulate metabolism and weight.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can worsen autoimmune conditions; try yoga or meditation.
- Regular Check-ups: Especially if you have a family history.
- Avoid Toxins: Limit exposure to endocrine disruptors in plastics or pesticides.
For “thyroid health tips” or “preventing thyroid disease,” focus on balance, a healthy lifestyle goes a long way.
Helpful Products from Amazon for Thyroid Support
While no product replaces medical treatment, certain items can complement your thyroid health routine under doctor supervision. Here are a few Amazon recommendations:
1. Iodine Drops: MaryRuth’s Organic Liquid Iodine Supplement is vegan and easy to dose, helping those with mild deficiencies. Great for adding to water daily.
👉Get it Here: MaryRuth iodine drops
2. Selenium Supplements: NOW Foods Selenium 200 mcg capsules support hormone conversion. It’s a bestseller for immune and thyroid health.
👉Get it Here: NOW selenium supplement
3. Thyroid Health Books: “The Thyroid Reset Diet” by Dr. Alan Christianson offers practical advice on reversing thyroid disease through food. Informative and empowering.
👉 Get it Here: Thyroid Reset Diet book
4. Neck Massager for Comfort: If goiter or inflammation causes discomfort, a cordless neck massager like the RENPHO model provides relief with heat therapy.
👉 Get it Here: RENPHO neck massager
Remember, these are supportive tools, consult your doctor to avoid interactions or over-supplementation, especially with iodine, which can worsen some conditions.
Final Thoughts on Thyroid Health
The thyroid gland may be small, but its impact on your daily life is enormous. From regulating metabolism to influencing mood, understanding its functions and potential disorders empowers you to take charge of your health. If you’re dealing with symptoms or just want to optimize your well-being, start with a doctor’s visit and incorporate healthy habits. With proper management, most thyroid conditions are highly treatable, allowing you to live vibrantly.