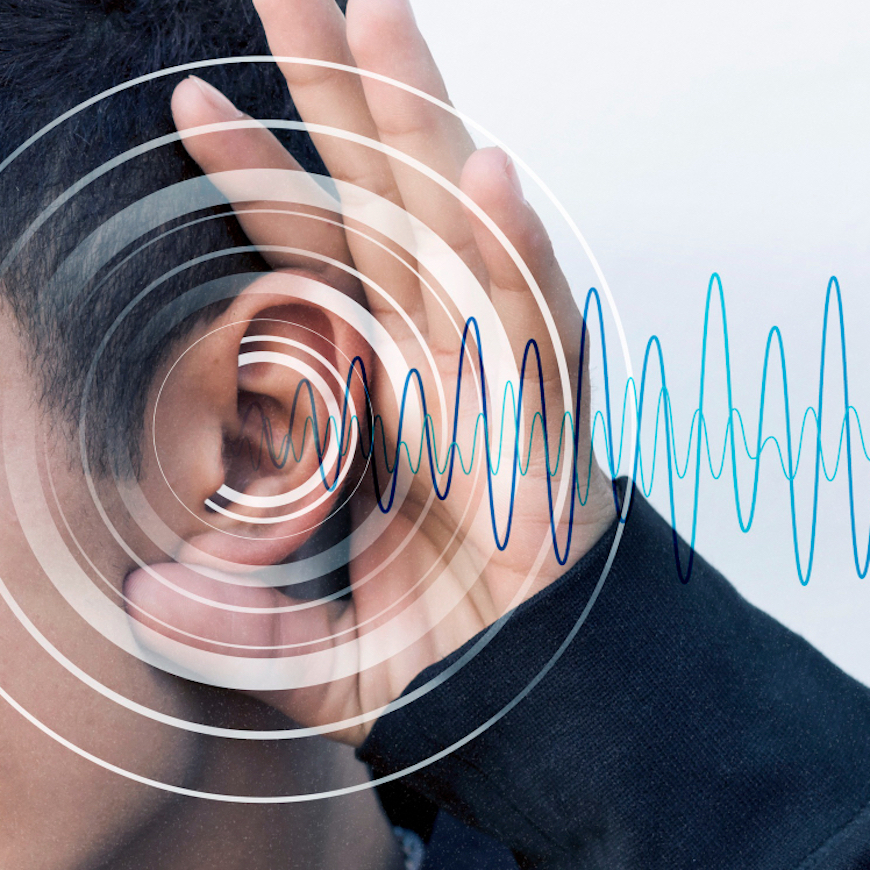
Tinnitus is the perception of sounds that have no external source of noise. These sounds can vary greatly and might include ringing, buzzing, roaring, or hissing. These sounds are internal and have no external source, which is why they are sometimes called phantom sounds.
Ear damage and exposure to loud noises are common causes of ringing or humming sounds in the ears. Less commonly, tinnitus can result from medications or thyroid disease.
It can be quite frustrating, especially if it interferes with other sounds around you. Anxiety and stress can also worsen the condition, impacting your overall well-being.
Tinnitus can occur in one or both ears and, while it can happen at any age, it is more frequently found in older adults.
Types of tinnitus
Generally, it is classified into two main types:
- Subjective Tinnitus: This is the most common form, where the sounds heard—such as ringing, roaring, or buzzing—are only audible to the person experiencing them. Subjective tinnitus can be caused by a variety of factors, including hearing loss or ear infections.
- Objective Tinnitus: Less common than subjective tinnitus, this type involves sounds that can also be heard by a physician during an examination. Objective tinnitus is often linked to physical issues such as abnormal blood vessels or muscle contractions near the ear. In this case, the sounds you hear often match the rhythm of your heartbeat.
Tinnitus causes
Damage to the inner ear is a frequent cause of this disease.
Here’s how it works: Your middle ear captures sound waves, which then travel to the inner ear, where they are converted into electrical impulses sent to your brain. You perceive these sounds only after your brain processes these electrical signals.
When the inner ear is damaged, it can interfere with the normal hearing process, resulting in tinnitus. Additionally, damage to the small bones in the middle ear or the eardrums can impact sound conduction. Additionally, tumors in the ear or on the auditory nerve might contribute to tinnitus.
Frequent exposure to very loud noises is another common cause. For example, people who use heavy machinery like jackhammers or chainsaws are at a higher risk. Exposure to loud music through headphones can also result in temporary tinnitus. In other words, when you are exposed to a high level of sound this may cause damage to your ears could be one of the main issues for having tinnitus.
Medical conditions
Throughout this paragraph you will be able to know what are the medical conditions that can lead to tinnitus include:
- Ear infections
- Excess earwax, which can interfere with hearing
- Age-related hearing loss
- Muscle spasms in the middle ear
- Thyroid disease
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol
- Head and neck injuries
Less common causes of tinnitus can include aneurysms and palatal myoclonus, which is characterized by muscle spasms in the roof of the mouth.
Tinnitus diagnosis
Diagnosing tinnitus can be challenging because you are typically the only one who hears the sounds it produces.
To diagnose tinnitus, a primary care physician or audiologist will begin with an examination of your ears and a hearing test. Therefore, for more explanation about the test. First, during the test, you’ll wear headphones through which sounds will be played one ear at a time. You will signal when you hear each sound, typically by raising your hand or using a similar gesture.
The results will help the doctor assess your hearing ability compared to what is expected for someone of your age and sex. They might also use imaging tests, such as CT scans or MRIs, to check for irregularities or damage. Plain film X-rays may not always reveal tumors, blood vessel disorders, or other abnormalities that could impact your hearing.
Be aware that in certain cases, despite these tests, the exact cause of your tinnitus may remain unidentified.
Tinnitus treatment
If medications are the cause, the doctor might suggest alternatives to restore your hearing. Various treatments and remedies for tinnitus include:
Sound-Based Therapies
- Noise-Canceling Machines: These devices provide relaxing sounds that can mask the ringing, buzzing, or roaring you hear.
- Masking Devices: Inserted into your ear, these devices work similarly to hearing aids to help mask tinnitus sounds.
Lifestyle Changes
- Stress Reduction: While stress doesn’t cause tinnitus, it can make it worse. Engaging in hobbies or talking with loved ones can help manage stress.
- Avoid Loud Noises: Limiting exposure to loud sounds can reduce the severity of tinnitus.
Hearing Aids
- Hearing Aids: For those with hearing loss in addition to tinnitus, hearing aids can amplify external sounds and help balance the perception of internal noises.
Preventing Tinnitus
- Protect Your Ears: Avoid loud noises and use ear protection around sounds exceeding 85 decibels (dBA), such as city traffic or construction sites.
- Monitor Volume Levels: Keep the volume of your TV, radio, and personal music player at moderate levels.
- Regular Hearing Tests: Schedule regular check-ups to detect and address any ear issues early on.
In the end, you have to keep your health under examination, don’t let your ear be exposed to high sound levels, even during working time. Try to avoid any additional medication that can harm your ears, and leave stress out of your life as much as possible. Moreover, you have to be aware of taking into consideration all written items mentioned in this article to keep your lifestyle as good as possible.