You can get vitamin D through the sun, food and supplements. To help your body produce the vitamin from the sun, researchers recommend exposing your skin to the sun for 5 to 30 minutes a day or twice a week without using sunscreen. days. However, exposure to the sun without sunscreen can cause skin damage and increase the risk of skin cancer.
while you can get the vitamin from the sun, it’s also important to eat foods rich in vitamin D, including dairy products, fatty fish, eggs, and mushrooms. It is an important nutrient for health. Vitamin D, like vitamins A, E, and K, is a fat-soluble vitamin, meaning that the digestive tract absorbs the vitamin from dietary fat and transports it into the bloodstream.
From there, the vitamin is stored in the liver and fat tissue for later use. This key nutrient supports your muscles, tendons and immune system, and helps absorb calcium, one of the main building blocks of bones.
Foods High in Vitamin D
You may notice that each food product has a nutrition label that shows the amount of calories, fat and other nutrients in each serving.
The daily value of vitamin D on food labels is 20 mcg or 800 IU for adults and children 4 years and older. The vitamin percentages you see on food labels are based on these values.
1- Mushrooms

Mushrooms exposed to sunlight have more vitamin D.
The vitamin content in mushrooms exposed to UV light decreases due to storage and cooking. Researchers recommend eating mushrooms before the “best before” date to get more than 10 micrograms of vitamin D per 100 grams. This level is higher than most foods containing the vitamin, which is equivalent to the daily requirement.
For example, a UV-visible mushroom called Monterey Mushrooms provides 100% of your daily dose of vitamin D for every 10 mushrooms.
You can increase the vitamin content in store-bought mushrooms by placing them under sunlight for a few hours. Simply place them with their gills facing upward in direct sunlight, and they will naturally produce more vitamin D2.
Incorporating mushrooms into your diet, especially sun-exposed varieties, is a great way to boost vitamin levels, particularly for those following plant-based or vegetarian diets.
2- Fish

Fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, sardines, and tuna, are rich in several essential vitamins that play key roles in maintaining overall health. One of the most important vitamins found in fish is vitamin D, which is crucial for bone health, immune function, and mood regulation.
Vitamin D helps the body absorb calcium, making it vital for strong bones and teeth. Fatty fish are one of the few natural food sources of the vitamin, which is particularly beneficial for people who don’t get enough sunlight exposure.
3- Eggs

Do eggs contain vitamin D? A serving of two eggs provides 82% of the daily value for the vitamin, making eggs one of the highest-rich foods. Maintaining a regular egg intake, such as 7 eggs per week, can help reduce winter vitamin D deficiency due to less natural vitamin D obtained from the sun.
Although eating 7 eggs per week is good, eating too much does not have any negative consequences. A recent study found that teenagers who ate 12 eggs per week did not experience significant changes in body weight or blood sugar compared to those who ate 7 eggs per week.
Most of the protein in an egg is in the white, while the fat, vitamins and minerals are primarily found in the yolk.
Vitamin D in chicken feed and exposure of liquid egg yolk to UV light increases the vitamin content of eggs.
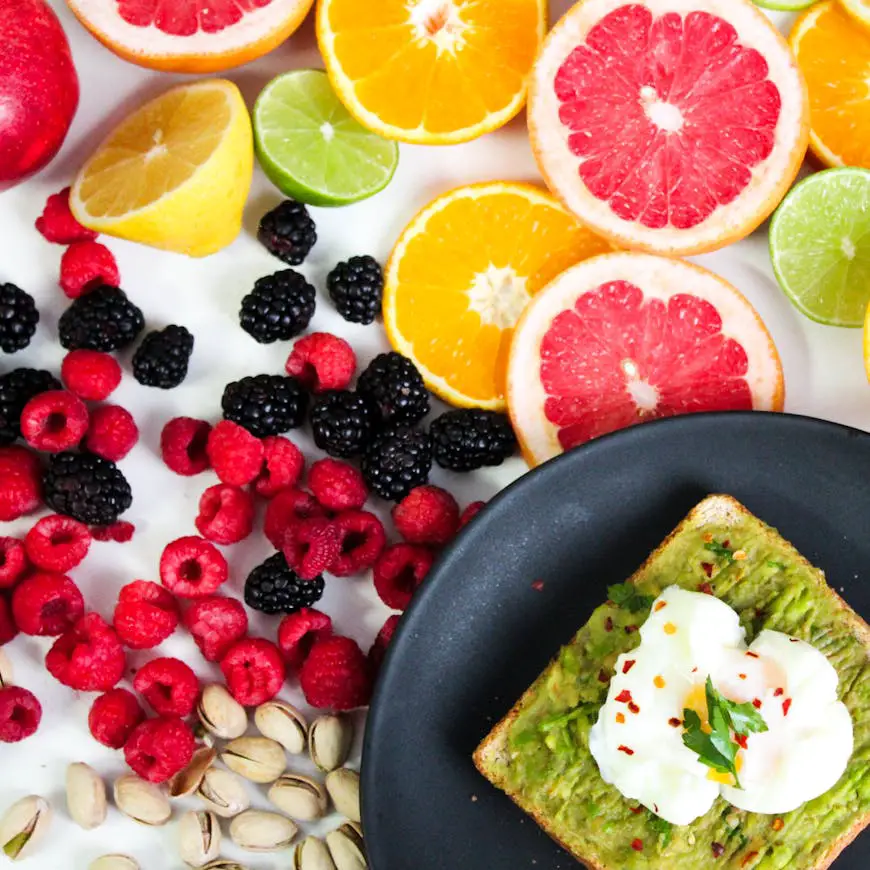
Healthy breakfast rich in Vitamin D: Avocado Toast with Poached Eggs
4- Milk

Although milk does not contain vitamin D, it is a good source of calcium. These two nutrients work well together because the vitamin helps bones absorb calcium, strengthens bones and prevents rickets and osteomalacia.
Non-dairy milk, like breast milk, is very low in vitamin D, so people who drink non-dairy milk should try to get vitamin D from oily fish or supplements. The risk of getting too much the vitamin from fortified milk is very low.
Consuming milk regularly, particularly fortified varieties, is an easy way to boost your intake of these important vitamins, promoting bone health and overall well-being.
5- Cereal Fortified with Vitamin D

Cereal fortified with vitamin D can be an excellent and convenient way to boost your intake of this essential nutrient, especially for those with limited sun exposure.
Fortified cereals, when paired with milk (which may also be fortified with vitamin D), provide a double boost of this essential vitamin, making breakfast a key opportunity to enhance vitamin intake and promote bone and immune health.
Additionally, fortified cereals often come with a range of other essential vitamins and minerals, such as B vitamins, iron, and fiber, contributing to a well-rounded meal. This makes them an ideal choice for breakfast or a quick snack, especially for those who may struggle to get enough nutrients from their diet.